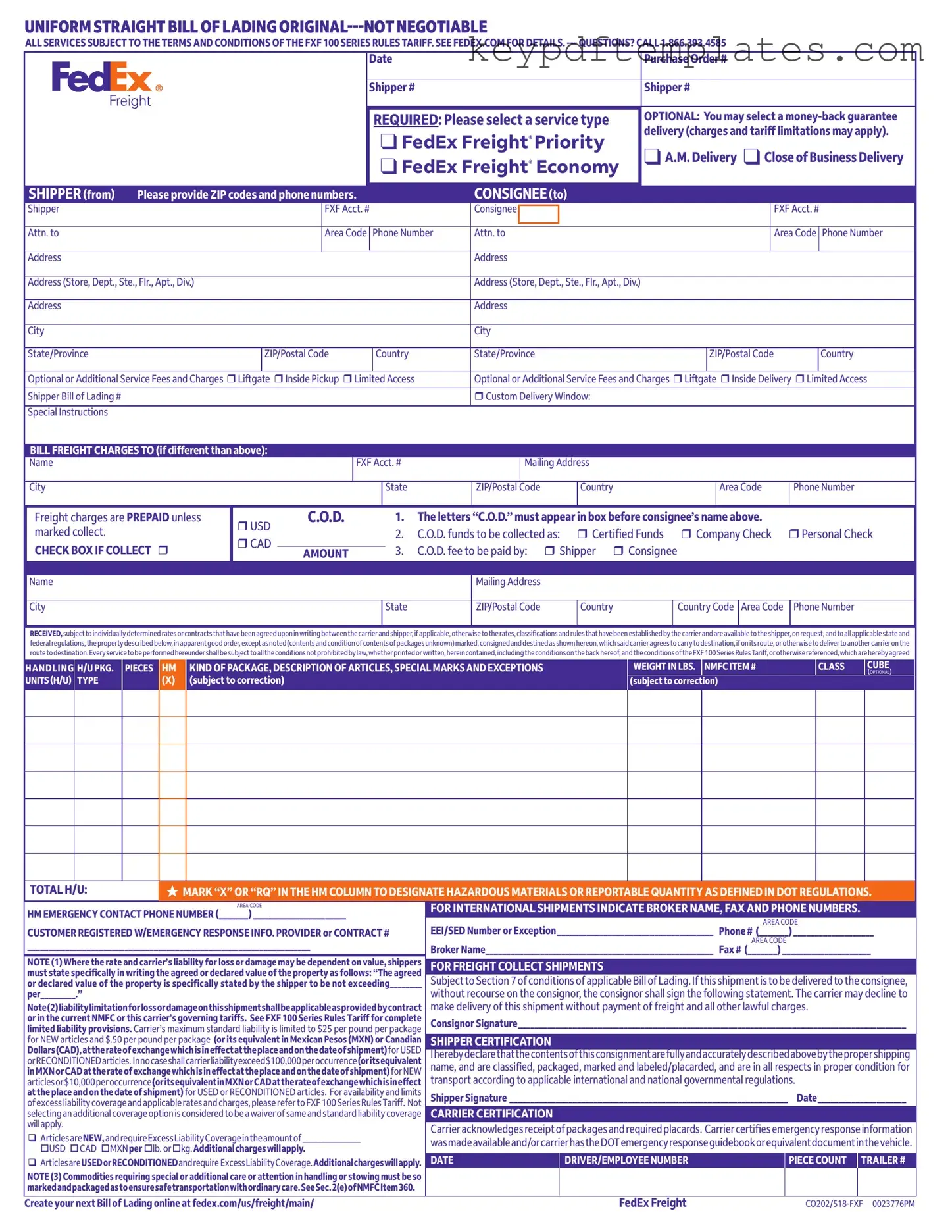
Get Fedex Bill Of Lading Form
Key takeaways
When filling out the FedEx Bill of Lading form, attention to detail is crucial. Here are key takeaways to ensure proper completion and usage:
- Service Type Selection: Clearly select the appropriate service type, such as FedEx Freight Priority or Economy. This choice impacts delivery speed and cost.
- Accurate Information: Provide complete and accurate information for both the shipper and consignee, including ZIP codes and phone numbers.
- Optional Services: Consider additional services like liftgate or inside delivery. These may incur extra fees but can enhance delivery efficiency.
- C.O.D. Details: If using Cash on Delivery (C.O.D.), specify the amount and payment method clearly to avoid delays.
- Hazardous Materials: Mark hazardous materials appropriately. Use "X" or "RQ" in the designated column to ensure compliance with regulations.
- Declared Value: If applicable, state the agreed or declared value of the shipment. This can affect liability in case of loss or damage.
- Signature Requirement: Ensure the shipper and carrier sign the document. This confirms agreement to the terms and conditions outlined.
- Emergency Contact: Provide emergency contact information for hazardous materials shipments. This is vital for safety during transit.
- Online Resources: Utilize online resources at fedex.com for guidance on creating your Bill of Lading and understanding service options.
Completing the FedEx Bill of Lading accurately can significantly impact the efficiency and safety of your shipment. Ensure all sections are filled out thoroughly to avoid potential issues.
Similar forms
- Uniform Commercial Invoice: Like the FedEx Bill of Lading, this document outlines the details of a sale, including the buyer, seller, and items being sold. It serves as a record for both parties and is often used for shipping and customs purposes.
- Shipping Manifest: This document lists all the items being shipped in a particular shipment. Similar to the Bill of Lading, it provides information on the sender, recipient, and contents of the shipment.
Operating Agreement: For those establishing an LLC, the comprehensive Operating Agreement guide outlines critical management structures and procedures to help prevent disputes.
- Air Waybill: Used primarily for air freight, the Air Waybill functions like a Bill of Lading, detailing the shipment's route, contents, and terms of transport. It serves as a contract between the shipper and the airline.
- Freight Bill: This document details the charges for transporting goods. It is similar to the Bill of Lading in that it outlines the shipment's details and the costs involved, ensuring both parties understand the financial obligations.
- Delivery Receipt: Upon delivery of goods, this document is signed by the recipient to confirm receipt. It serves as proof of delivery, much like the Bill of Lading, which also acts as a receipt for the shipper.
- Export Declaration: Required for international shipments, this document provides information about the goods being exported. It shares similarities with the Bill of Lading in that both documents are essential for customs clearance.
- Customs Invoice: This document is used for international shipments to provide customs officials with details about the contents of a package. Like the Bill of Lading, it helps facilitate the shipping process across borders.
- Warehouse Receipt: Issued by a warehouse to acknowledge the storage of goods, this document is similar to a Bill of Lading as it serves as proof of ownership and details the items stored.
- Purchase Order: This document is issued by a buyer to a seller, indicating the items they wish to purchase. It is similar to the Bill of Lading in that it outlines the transaction details and helps track shipments.
- Pro Forma Invoice: Often used in international trade, this document provides an estimate of the costs associated with a shipment. It shares characteristics with the Bill of Lading by detailing the items and terms of sale.
Misconceptions
Misconceptions about the FedEx Bill of Lading form can lead to confusion and potential issues with shipments. Here are nine common misconceptions, along with explanations to clarify them:
- The Bill of Lading is only for freight shipments. Many believe this document is only necessary for large freight shipments. In reality, it is used for all types of shipments, including smaller packages, to ensure proper handling and delivery.
- All shipments automatically come with insurance coverage. Some think that shipping with FedEx includes automatic insurance for lost or damaged items. However, liability coverage is limited, and additional insurance must be purchased for higher value items.
- The sender is always responsible for shipping costs. It is a common belief that the shipper always pays for shipping. However, the Bill of Lading allows for various payment options, including collect shipments where the consignee pays the freight charges.
- Hazardous materials can be shipped without special markings. Some people assume that they can ship hazardous materials without following specific regulations. This is incorrect; proper labeling and documentation are required for safety and compliance.
- The Bill of Lading is not a legal document. Many think this form is just a receipt. In fact, it serves as a legal contract between the shipper and carrier, outlining responsibilities and liabilities.
- Delivery times are guaranteed. There is a misconception that all services listed on the Bill of Lading guarantee delivery times. While some services offer time-specific deliveries, others may be subject to delays due to various factors.
- Customs paperwork is unnecessary for international shipments. Some believe that completing the Bill of Lading is sufficient for international shipping. However, additional customs documentation is often required to ensure compliance with international regulations.
- Once shipped, the sender cannot make changes. It is a common misconception that no changes can be made after the Bill of Lading is issued. In fact, shippers can request modifications, but it may require additional documentation and could incur fees.
- The form can be filled out in any order. Some think that the order of information on the Bill of Lading does not matter. However, completing the form in the correct order is essential to avoid delays and ensure accurate processing.
Understanding these misconceptions can help ensure a smoother shipping experience with FedEx.
More PDF Templates
Konami Decklist - Ensure proper spacing between card names for clarity.
A Texas Motorcycle Bill of Sale form is a legal document used to record the transfer of ownership of a motorcycle between a buyer and a seller. This form outlines essential details regarding the motorcycle, including its make, model, and Vehicle Identification Number (VIN). Having a properly completed bill of sale provides both parties with proof of the transaction and protects their interests. To obtain this important document, you can use the Motorcycle Bill of Sale form.
Cg2010 Form - Serves as a crucial reference point for assessing coverage limitations and responsibilities.
Form Specs
| Fact Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Document Type | The FedEx Bill of Lading is a Uniform Straight Bill of Lading, which is not negotiable. |
| Governing Terms | All services are subject to the terms and conditions outlined in the FXF 100 Series Rules Tariff. |
| Service Options | Shippers can select from various service types, including FedEx Freight® Priority and Economy. |
| C.O.D. Options | Cash on Delivery (C.O.D.) options are available, including certified funds and checks. |
| Liability Limits | Carrier liability is generally limited to $25 per pound for new articles and $0.50 for used articles. |
| Emergency Contact | For hazardous materials, an emergency contact number must be provided on the form. |
Documents used along the form
The FedEx Bill of Lading is a crucial document for shipping freight. It outlines the terms of the shipment and serves as a receipt for the goods. However, several other forms and documents may accompany it to ensure smooth transportation and compliance with regulations. Here’s a list of commonly used documents in conjunction with the FedEx Bill of Lading.
- Commercial Invoice: This document details the transaction between the shipper and the consignee. It includes information about the goods, their value, and payment terms.
- Packing List: A packing list itemizes the contents of the shipment. It helps the consignee verify the delivery and can assist customs officials during inspections.
- Freight Manifest: This is a comprehensive list of all shipments being transported on a specific vehicle. It helps carriers track and manage multiple shipments.
- Shipping Label: This label contains essential information for the shipment, including addresses, tracking numbers, and barcodes. It ensures that packages are delivered to the correct destination.
- Residential Lease Agreement: This essential document outlines the terms and conditions for renting residential property and is critical for protecting rights and ensuring a smooth rental experience. For more details, see Top Forms Online.
- Export Declaration: Required for international shipments, this document provides customs with information about the goods being exported, including their value and destination.
- Insurance Certificate: If the shipment is insured, this certificate proves coverage. It outlines the terms of the insurance and the value of the goods covered.
- Hazardous Materials Declaration: For shipments containing hazardous materials, this declaration informs carriers and handlers about the nature of the materials and necessary precautions.
Each of these documents plays a vital role in the shipping process. They help ensure that shipments comply with legal requirements and that all parties involved understand the terms of the transaction. Proper documentation can prevent delays and issues during transit.